Marijuana News
The post AG Sessions: Cole Memo is Valid, But Skeptical of Medical Cannabis appeared first on Cannabis Industry Journal.
]]>This time around, Sessions’ words on legal cannabis were more carefully chosen. “The Cole Memorandum set up some policies under President Obama’s Department of Justice about how cases should be selected in those states and what would be appropriate for federal prosecution, much of which I think is valid,” Sessions told reporters. The Cole Memo essentially set up a framework for states with legal cannabis laws to avoid federal enforcement of the Controlled Substances Act.

These comments do fall in line with some of his previous statements, like suggesting he wants to uphold federal law. During the speech in Richmond, Sessions denied any possibility that cannabis could be a solution to the opioid crisis. “I reject the idea that America will be a better place if marijuana is sold in every corner store,” says Sessions. “And I am astonished to hear people suggest that we can solve our heroin crisis by legalizing marijuana – so people can trade one life-wrecking dependency for another that’s only slightly less awful.” These statements echo much of what White House press secretary Sean Spicer said weeks ago, citing the opioid crisis as possibly linked to recreational cannabis consumption.
Sessions admitted to reporters that he acknowledges the benefits of medical cannabis, but says he is still skeptical of the idea, saying it has been overhyped. “It’s possible that some dosages can be constructed in a way that might be beneficial,” says Sessions. “But if you ever just smoke marijuana, for example, where you have no idea how much THC you’re getting it’s probably not a good way to administer a medicinal amount- so, forgive me if I’m a bit dubious about that.” Sessions pontificating the medical efficacy of delivery methods for cannabinoids could suggest he is trying to familiarize himself more with the science behind medical cannabis.
According to a Politico article, Sessions privately told senators that he would respect states’ rights on the issue and uphold Obama-era policies, perhaps referring to the Cole Memo. While Sessions’ most recent remarks could signal a less aggressive approach toward legal cannabis, he still makes his position clear as a Drug War stalwart. “Our nation needs to say clearly once again that using drugs will destroy your life,” Says Sessions.
The post AG Sessions: Cole Memo is Valid, But Skeptical of Medical Cannabis appeared first on Cannabis Industry Journal.
]]>The post Going Beyond POS: Innovations in Dispensary Software appeared first on Cannabis Industry Journal.
]]>At their SE 7th Ave location in Portland, Oregon, Cannabliss & Co. uses Baker software to better connect with their customers and track sales. According to Kevin Mahoney, manager of that dispensary, they use Baker’s software for things like their online menu, online ordering, text alerts and a rewards program.

Located in an historic firehouse built in 1913, Cannabliss & Co. was Oregon’s very first medical cannabis dispensary. Now that they offer both recreational and medical cannabis, their product inventory has expanded, their sales have grown and they have a wider customer base.
 After using Baker’s software platform for almost a year now, Mahoney says he has seen great ROI on text alerts and the analytics. The online ordering and menu features have not only highlighted sales trends, but have made budtender-customer interactions easier. “We don’t want our budtender using the menu as a focal point of the conversation, but this allows for us to highlight particular specials or strains on our menu that gets eye attention right when the customer gets in,” says Mahoney. “Moving past the point of sale, it allows another conversation to happen organically, which keeps the customer engaged.”
After using Baker’s software platform for almost a year now, Mahoney says he has seen great ROI on text alerts and the analytics. The online ordering and menu features have not only highlighted sales trends, but have made budtender-customer interactions easier. “We don’t want our budtender using the menu as a focal point of the conversation, but this allows for us to highlight particular specials or strains on our menu that gets eye attention right when the customer gets in,” says Mahoney. “Moving past the point of sale, it allows another conversation to happen organically, which keeps the customer engaged.”
On average, Baker sees conversion rates close to a 5% range per campaign. “That check in option is phenomenal; we get to see how many people actually came into the store from any given text alert,” says Mahoney. “In my mind, text alerts are preferable to email alerts; they can’t be marked as spam, it is easy to delete or opt out and takes much less time.”

Mahoney says the online ordering feature that Baker offers is a big selling point too. “Having an ordering service is absolutely terrific,” says Mahoney. “They can come in and out in less than five minutes with their full order by using the online ordering portal.” Mahoney says they see a real draw in this feature because it lets customers treat their dispensary like a takeout window at a restaurant.
Baker just launched a software platform designed for delivery service that a dispensary in Bend, Oregon has been using for two months now. With Portland legalizing cannabis delivery services recently, Mahoney is eyeing Baker’s software for his online ordering and delivery. “When the time comes, that is something we are very interested in pursuing.”

In August of 2016, Baker secured $1.6 million in seed funding, led by Former Salesforce Executive Michael Lazerow, according to a press release. “Baker has created a solution that is clean and easy to use and can help dispensary owners engage their shoppers like never before – online, mobile, social and in-store,” says Lazerow. “I witnessed first-hand how Salesforce supercharges its customers’ businesses and I’m inspired to see Baker driving the entire cannabis industry forward with this same intelligent approach.” In 18 months of business, Baker has worked with hundreds of dispensaries, helping them build better connections with over 100,000 customers. At Baker, we believe the cannabis shopping experience should be as comfortable and personalized as it has become in every other retail environment,” says Joel Milton, chief executive officer at Baker. “With expertise in cannabis, data and technology we have created an industry-specific tool that allows dispensaries and brands engage with customers and build brand loyalty through a personalized shopping experience.”

According to Eli Sklarin, director of marketing at Baker, the number one reason why patients and customers choose a dispensary is because of products on the shelf. “We originally started the platform in 2014 so people could order ahead and wouldn’t have to wait in lines at the dispensary,” says Sklarin. “In 2015, we saw more dispensaries than fast food establishments in many cities. Once inventory started to settle down, we saw a need for the dispensary to better connect with their customers.” The three core products that Baker offers are online ordering, connect SMS & email and the check in & loyalty program.
Their entire suite of software options is specific to the cannabis retail space. “Our customizable program is designed to help dispensaries catch customers and keep them coming back,” says Sklarin. “The software can give a snapshot of who their customers are, insights into the overall health of their dispensary, sales per day of the week, monthly promotions and other basic analytics that help them understand their customers.” Things like strain alerts can help retain customers, allowing dispensaries to notify certain groups of customers when products are back in stock. Whether it’s a customer who prefers a particular brand of edibles or concentrates, these software tools can help dispensaries get the right message to the right customer.
The post Going Beyond POS: Innovations in Dispensary Software appeared first on Cannabis Industry Journal.
]]>The post Shimadzu Launches Cannabis Analyzer for Potency appeared first on Cannabis Industry Journal.
]]>
The instrument is designed to test for 11 cannabinoids in less time and with greater ease than traditional HPLC instruments. In the press release, they claim “operators are now able to produce accurate results with ease, regardless of cannabis testing knowledge or chromatography experience.” One very unique aspect of the instrument is the lack of experience required to run it, according to Bob Clifford, general manager of marketing at Shimadzu. “We have our typical chromatography software [LabSolutions] with an overlay that allows the user to analyze a sample in three simple steps,” says Clifford. Those in the cannabis industry that have a background in plant science, but not analytical chemistry, could run potency analyses on the instrument with minimal training. “This overlay allows ease of use for those not familiar with chromatography software,” says Clifford.
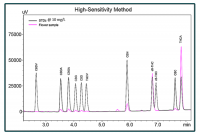
The instrument can determine cannabinoid percentages per dry weight in flower concentrates and edibles. “Once you open the software, it will get the flow rate started, heat the column up and automatically begin to prep for analysis,” says Clifford. Before the analysis begins, information like the sample ID number, sample name, sample weight, extraction volume and dilution volume are entered. After the analysis is complete all the test results are reported for each sample.
Because laboratories wouldn’t have to develop quantitative testing methodology, they argue this instrument would save a lot of time in the lab. “After one day of installation and testing, users are equipped with everything they need to obtain cannabis potency results,” states the press release. According to Clifford, method development for potency analysis in-house can take some labs up to three months. “We can bring this instrument to the lab and have it ready for testing almost immediately,” says Clifford. “The methods for this instrument were developed by a team of twenty scientists working on different platforms at our Innovation Center and was tested for ruggedness, repeatability and quantitative accuracy.”

The instrument’s workflow is designed to meet three methods of analysis depending on testing needs. The High Throughput method package can determine quantities of ten cannabinoids with less than eight minutes per sample. The method was developed in collaboration with commercial testing laboratories. The High Sensitivity method package adds THCV to that target analyte list with ten minutes per analysis. The method provides the sharpest chromatographic peaks and best sensitivity. The High Resolution method package offers full baseline resolution for those 11 cannabinoids in less than 30 minutes per analysis and the ability to add cannabinoids to that target list if regulations change.
The press release states the interface should allow users to reduce the number of steps needed in the analysis and simplify the workflow. The instrument comes with a three-year warranty, preventative maintenance plan and lifetime technical support.
The post Shimadzu Launches Cannabis Analyzer for Potency appeared first on Cannabis Industry Journal.
]]>The post Cannabis-Specific Certified Reference Materials appeared first on Cannabis Industry Journal.
]]>The fact that a certificate accompanies a reference material does not qualify it as a CRM. The reference material must be produced in accordance with ISO Guide 34 specifications by an accredited manufacturer. Adam Ross, key account manager and organic specialist at LGC Standards, says accreditation is a big part of bringing legitimacy to cannabis testing. “For a laboratory to receive an ISO 17025 accreditation, they must purchase their RMs from an ISO 17025 manufacturer. The best option is to purchase an ISO Guide 34 manufactured CRM,” says Ross. “It is particularly important for testing requirements, such as potency, pesticides, etc., where quantitation is expected, to use properly certified quantitative reference materials.” LGC Standards, a 175-year-old company, is one of those manufacturers that invested the time and money to achieve ISO Guide 34 accreditation and offers a spectrum of CRMs for cannabis testing.

The major advantage to using a proper CRM is an increased level of credibility. Auditors recognize the value of using a CRM which can add to the integrity of the results produced. The regular use of certified reference standards along with proper training, methodology and instrumentation, will facilitate a result that has the least amount of uncertainty and is more defendable. “The regular use of certified reference standards will help ensure products that go to market are safe to consume,” says Ross.
With regard to potency analyses, Ross has some key insights to help a laboratory better utilize CRMs. “My advice? Don’t mix the cannabinoids; labs analyzing by GC/FID have discovered that some of the cannabinoids will co-elute. Also, they have a short shelf life when mixed together,” says Ross. “Cannabinoid analysts should use GC/MS or LC/MS for their analysis or analyze the cannabinoids individually,” says Ross.
 So what happens if a cannabis lab uses non-certified reference materials? Labs might save money in the short term. CRMs are slightly more expensive than a non-certified reference material, but will increase the defensibility of a lab’s data. Using a reference material created in-house or from a non-accredited vendor can lead to less-than-accurate results. A non-certified reference material has a greater chance of being made incorrectly. The publication of incorrect data damages the credibility of the testing lab and could lead to legal action against the lab from damaged parties.
So what happens if a cannabis lab uses non-certified reference materials? Labs might save money in the short term. CRMs are slightly more expensive than a non-certified reference material, but will increase the defensibility of a lab’s data. Using a reference material created in-house or from a non-accredited vendor can lead to less-than-accurate results. A non-certified reference material has a greater chance of being made incorrectly. The publication of incorrect data damages the credibility of the testing lab and could lead to legal action against the lab from damaged parties.
One of the major challenges for the cannabis testing industry is the variation in state-to-state regulations. Ross says that Oregon’s regulations are pretty comprehensive and that other states should look to the Oregon Environmental Laboratory Accreditation Program (ORELAP) for guidance. According to Ross, ORELAP would like to see higher quality standards with legitimate traceability. Utilizing CRMs the correct way will help laboratories achieve greater accuracy.
Here are some tips for using CRMs appropriately:
- Always bring your standards to room temperature before making a dilution.
- Matrix matched calibration standards provide more accurate quantitation. Prepare standards in the solvent from extracted blank matrices.
- Always bracket your analytical runs with continuing calibration verification standards. Proving that your instrument remained calibrated during the run gives your data more credibility.
Analytical chemists purchase CRMs for three primary uses in the testing lab:
- To calibrate the instrument that will be used to perform the testing
- To confirm the instruments continuing calibration throughout the analytical process
- For analytical quality control or “spikes”
Typically, labs will spike known concentrations of the analytes of interest into a control sample and regular samples with the intent of testing analytical efficiency. Recoveries of analytes from the spiked control sample tell the chemist how well the analytical method is working. The spiked samples (matrix spikes) demonstrate to what extent the sample matrix (the consumable being tested) is influencing the results of the analytical procedure.
CRMs could be described as the nexus between cannabis testing results, the human element and the instrumentation used in an analysis. By using a cannabis-specific CRM, the cannabis testing community can demonstrate tangible improvements in accuracy and legitimacy.
The post Cannabis-Specific Certified Reference Materials appeared first on Cannabis Industry Journal.
]]>The post ASTM International Launches Cannabis Committee appeared first on Cannabis Industry Journal.
]]> ASTM International meets the World Trade Organization (WTO) principles for developing international standards, and maintains the attributes outlined in the National Technology Transfer and Advancement Act (NTTAA) for a voluntary consensus standards development organization. ASTM International is known throughout a variety of industries for creating voluntary consensus standards for products, systems, services and materials. ASTM standards are used globally in research and development, product testing, quality systems, commercial transactions, and more.
ASTM International meets the World Trade Organization (WTO) principles for developing international standards, and maintains the attributes outlined in the National Technology Transfer and Advancement Act (NTTAA) for a voluntary consensus standards development organization. ASTM International is known throughout a variety of industries for creating voluntary consensus standards for products, systems, services and materials. ASTM standards are used globally in research and development, product testing, quality systems, commercial transactions, and more.

On January 18th, 2017, the American Public Health Association hosted thirteen industry stakeholders representing state laboratories, standards developers, research institution, academia, cultivation centers, auditors and software compliance providers, according to Lezli Engelking, founder of the Foundation of Cannabis Unified Standards (FOCUS), who is involved and familiar with the process. The planning meeting discussions included a summary of where the request was initiated, why a standards activity was necessary and the results of ASTM’s exploratory efforts. At the conclusion of the planning meeting, it was decided by vote, that ASTM should move forward with the activity.
On February 28th, 2017, roughly 60 stakeholders and cannabis industry representatives met at ASTM International’s headquarters in Conshohocken, Pennsylvania. The volunteer committee on cannabis, designated D37 by ASTM, is a result of inquiries flooding the company regarding cannabis since 2015, states the press release.
The committee will focus on six technical areas, forming subcommittees:
- Indoor and outdoor horticulture and agriculture,
- Quality management systems,
- Laboratory,
- Processing and handling,
- Security and transportation, and
- Personnel training, assessment, and credentialing.
Dr. Ralph Paroli, immediate past chairman of the board and director of R&D in measurement science and standards at the National Research Council of Canada, was voted to serve as the committee’s first chairman. “With its decades of experience in industries such as pharmaceuticals, medical devices, packaging, agriculture, pesticides, and more, ASTM International is the perfect place for standards development for the cannabis industry,” says Paroli.
Pending ASTM International board of directors’ approval (anticipated late April 2017), a shift of standards development efforts has been made from FOCUS to the ASTM International technical committee D37 on cannabis and its products and processes.
“FOCUS could not be more pleased by ASTM’s decision to further the development of internationally harmonized cannabis standards,” says Engelking. “This is desperately needed, and an enormous step in the right direction of legitimizing the cannabis industry. We are thrilled FOCUS standards will be included, and honored to be a part of this exciting process.” During this transition period, interested stakeholders can get directly involved through the FOCUS website and then follow directions provided by FOCUS.
According to Engelking, third-party, cannabis-specific certifications for cultivation, retail, extraction, infused products and laboratories are provided by FOCUS for cannabis businesses committed to providing safe, consistent and quality products. FOCUS certification helps businesses decrease liability and risks, maximize efficiency, reduce costs and differentiate their brands.
“FOCUS encourage all stakeholders to participate in this important process,” says Engelking. “ASTM has an incredible standards development system in place that allows for many different levels of participation.” During 2017, ASTM is offering free temporary memberships. After 2017, stakeholders will need to join as a participating member.
The post ASTM International Launches Cannabis Committee appeared first on Cannabis Industry Journal.
]]>The post AG Sessions Ties Legal Cannabis to Violence, States React appeared first on Cannabis Industry Journal.
]]>
Photo: Gage Skidmore, Flickr
During a press conference last week, White House press secretary Sean Spicer told reporters “I do believe you will see greater enforcement of it,” referring to the enforcement of the Controlled Substances Act on recreational cannabis. He went on to make the distinction between medical and recreational use clear, while deferring to the Department of Justice, saying they will be looking further into the matter.
Much like press secretary Spicer incorrectly tied legal cannabis to the opioid crisis, Attorney General Sessions incorrectly tied legal cannabis to an increase in violence. “We’re seeing real violence around that,” says Sessions. “Experts are telling me there’s more violence around marijuana than one would think and there’s big money involved.” He did not discuss who those experts were or how he came to that conclusion. There are a number of studies refuting his claims, suggesting no causal link between legal cannabis and violence, with one study even suggesting a reduction in violent crimes after legalizing cannabis.

Image via Youtube
Sessions has not mentioned any specific policy actions that he would take on the enforcement of federal law. “We’re going to look at it. … And try to adopt responsible policies,” says Sessions. Jeff Sessions making these comments should come as no surprise as he expressed his disdain for cannabis a number of times and has been known to be a Drug War stalwart. President Trump promised during his campaign that he supports medical cannabis and the matter should be left up to the states. These recent comments by his newly appointed press secretary and attorney general suggest the administration may not honor that campaign promise.
Politicians in states that have legalized cannabis were quick to condemn the comments and uphold this as an issue of states’ rights. Colorado Governor John Hickenlooper told reporters legal cannabis is in their state’s constitution and he intends to uphold the will of the voters. Oregon State Rep. Knute Buehler (R-Bend) said in a press release, “I hope the new President and Attorney General keep their hands off Oregon’s marijuana law.” Regulators in Nevada have also said they plan to move forward with implementing legal recreational cannabis regulations, despite any federal actions or comments. Bob Ferguson, Washington State attorney general told the Associated Press, “We will resist any efforts to thwart the will of the voters in Washington,” and has requested a meeting with Sessions to discuss his policies. California Lt. Governor Gavin Newsom wrote a letter to President Trump telling him not to follow through on those threats of greater enforcement. “The government must not strip the legal and publicly supported industry of its business and hand it back to drug cartels and criminals,” Newsom wrote to Trump. “Dealers don’t card kids. I urge you and your administration to work in partnership with California and the other eight states that have legalized recreational marijuana for adult use in a way that will let us enforce our state laws that protect the public and our children, while targeting the bad actors.”
At this time, it remains unclear exactly how the Trump administration will address federal cannabis policy, but these vague and ominous statements from top federal officials continue to raise eyebrows in the cannabis industry. Until President Trump comes out with a clear stance on legal cannabis, those in the cannabis industry fear a federal crackdown on legal recreational cannabis is looming.
The post AG Sessions Ties Legal Cannabis to Violence, States React appeared first on Cannabis Industry Journal.
]]>The post WH Press Sec. Sean Spicer Hints at Trump Admin. Stance on Cannabis appeared first on Cannabis Industry Journal.
]]>Sean Spicer replied with more of the same of his previous statements regarding the Trump administration’s stance on cannabis legalization. “There are two distinct issues here: medical marijuana and recreational marijuana,” says Spicer. “I think medical marijuana- I’ve said before that the president understands the pain and suffering that many people go through, who are facing especially terminal diseases and the comfort that some of these drugs, including medical marijuana, can bring to them. And that’s one that congress, through a rider in 2011, I think put in the appropriations bill saying the Department of Justice wouldn’t be funded to go after them.” The rider in the appropriations bill he is referring to is the Rohrabacher–Farr amendment that became law in December of 2014, but must be renewed each fiscal year. That piece of legislation provides for exactly what he said- preventing the Justice Department from using funds for activity that might interfere with state’s legal medical cannabis programs. Regarding the actual conflict between federal and state laws, Spicer said “I do believe you will see greater enforcement of it,” referring to the Department of Justice enforcing the Controlled Substances Act.

Spicer went on to make some questionably ill-informed remarks, including linking recreational cannabis use to the opioid crisis. “There is a big difference between that [medical marijuana] and recreational marijuana,” says Spicer. “And I think that when you see something like the opioid addiction crisis blossoming in so many states around this country, the last thing we should be doing is encouraging people- there is still a federal law that we need to abide by… When it comes to recreational marijuana and other drugs of that nature.” Though those comments are unclear, it could suggest that Mr. Spicer believes in a possible link between recreational cannabis use and the opioid crisis, or at least grouping them in the same category. While there is not much evidence suggesting of the link he is referring to, a study published in 2014 in JAMA Internal Medicine, a peer-reviewed medical journal published by the American Medical Association, suggests a possible link between medical cannabis laws and the decrease in opioid overdoses.
Spicer continued to emphasize his distinction between medical and recreational use of cannabis. “I think there is a big difference between medical marijuana, which states where it is allowed, in accordance with the appropriations rider, have set forth a process to administer and regulate that usage versus recreational marijuana, and that is a very very different subject,” says Spicer. National Cannabis Industry Association executive director Aaron Smith issued a statement regarding Spicer’s comments.

“It would be a mistake for the Department of Justice to overthrow the will of the voters and state governments who have created carefully regulated adult-use marijuana programs,” says Smith. “It would represent a rejection of the values of economic growth, limited government, and respect for federalism that Republicans claim to embrace.” Smith says he was very disappointed when he heard press secretary Spicer relate cannabis to opioid addiction. “Science has discredited the idea that marijuana serves as any kind of gateway drug, and the addiction and death rates associated with opioids simply do not occur in any way with cannabis,” says Smith. In October 2016, NCIA published a report identifying cannabis as a possible solution to the opioid crisis.

Isaac Dietrich, chief executive officer of MassRoots, a social networking platform for medical cannabis, sees Spicer’s words having a direct impact on his business. “I have a feeling our stock is going to take a beating tomorrow, but that just creates an opportunity for investors who believe in the long-term trajectory of the cannabis market,” says Dietrich. He goes on to directly refute Spicer’s statements. “Colorado is one of the only states in the nation that is seeing a decline in opioid deaths — that’s not a coincidence,” says Dietrich. “Cannabis is a healthy alternative to pain pills and heroin, not a gateway to it.”
Press secretary Sean Spicer did not allow a reporter present at the press conference to ask a follow up question on the matter.
The post WH Press Sec. Sean Spicer Hints at Trump Admin. Stance on Cannabis appeared first on Cannabis Industry Journal.
]]>The post Implementing Real Science in Cultivation and Extraction appeared first on Cannabis Industry Journal.
]]>
The company prides themselves on attention to detail; the well versed team implements real science in their cultivation and extraction processes. Lincoln Fish, co-founder and chief executive officer of Outco, has more than 30 years of experience as an entrepreneur. Before entering the cannabis industry, Linc started and sold companies in the healthcare technology and nutraceutical spaces.

Fish’s experience with FDA regulations in nutraceuticals prepared him for running a business in such a tumultuous, highly regulated environment like cannabis. “One thing I took from the nutraceutical industry is how to present products to consumers and letting them know it is safe, effective and consistent,” says Fish. He says he noticed a serious lack of consistency in products. They tested 25 different vape cartridges, with their own oil, to find a consistent product they can use and know that consumers will safely and consistently get the same results. “There is a lot of room for more professionals and a lot of room for more science,” says Fish. “We try to position ourselves in a way that is consistent with where we think policy will go so we are very careful with recommendations from a scientific standpoint, patient information and product safety.”

According to Fish, they currently distribute cannabis products to about 75 licensed dispensaries in Orange County, San Diego and Los Angeles. With construction underway at their cultivation facility on Native American land, Fish says they plan to generate roughly 2600 pounds of cannabis each month. Gearing up for that in addition to the expanding recreational market requires some planning in advance, says Fish. Part of that plan is making sure quality controls are in place to keep consistency in the product quality and dosage. They are also actively seeking to open their distribution channels further.

“We are building out a full lab of our own in addition to third party testing to perform internal quality controls,” says Fish. Equipped with their own laboratory instrumentation like HPLC and GC, they hope to establish proper in-house quality controls as well as provide that resource to younger startup companies. As one of the founding partners of Canopy San Diego, an ancillary startup accelerator, Fish sees great potential in working with younger companies to get them off the ground. Fish met Outco’s vice president of extraction, Dr. Markus Roggen, at a Canopy San Diego event. It was there that they had the idea to build a startup accelerator for companies that actually touch the plant- extractors, cultivators and infused-product manufacturers, as opposed to a startup accelerator that would only help ancillary businesses.

Dr. Roggen, who is an organic chemist by training, heads up Outco’s supercritical CO2 extraction operation. “I came to the ‘art’ of cannabis extraction with an open, yet scientifically focused mind,” says Dr. Roggen. “My approach was to look past the myths and stories about extraction methods and focus on finding data, as there really wasn’t much available. I therefore, from the beginning, started to study the capabilities of our extraction equipment by chemometric methods.” Chemometrics is the science of relating measurements made on a chemical system or process to the state of the system via applications of mathematical methods. “Already the first sets of experiments showed that long-held beliefs in the cannabis community were inaccurate,” says Dr. Roggen. “For example the particle size of extracted material matters. Or that it is possible to preserve and even isolate terpenes by CO2 extraction methods.” With plans to have a full plant and analytical chemistry laboratory on site, they hope to perform more research that focuses on optimizing extraction processes.

Dr. Allison Justice leads their cultivation team with a background in greenhouse management and commercial horticulture. Dr. Justice says plants are grown, starting at a young age (seed or vegetative cutting), with the protection of biological control agents. “Biological control is a management strategy that entails the release of beneficial insects or fungi, such as parasitoids and predators, in order to suppress or regulate insect populations in greenhouses and grow rooms,” says Dr. Justice.

When implemented properly, this eliminates the need to use synthetic pesticides. “Biological control agents are not put in place to eradicate pest populations yet are applied as preventives to minimize plant damage and maintain their own populations.” They are constantly evaluating light types, spectrum and intensity to determine optimal ranges, according to Dr. Justice. They don’t use any pre-mixed “cannabis” nutrient supplements for their plants, instead they design an experiment to determine the desired levels and ratios of essential plant nutrients. “We have found it crucial to determine what ratios of nutrients the plant actually needs and by knowing this, we know how to manipulate the recipe determined by the plant’s given nutritional symptoms,” says Dr. Justice. Every type of adjustment in cultivation and extraction is based on results from experimentation rooted in legitimate science. Instead of guessing when it might be time to harvest, they use a water activity meter, logging and recording all the data to determine the appropriate time to trim and cure plants. Performing analytical testing at every step is key, says Fish.
Looking toward the recreational market, Fish sees an obvious opportunity to expand their wholesale operations substantially, with several larger new cultivation projects planned. “The key though is to produce flower and concentrate offerings with the same standards we employ for medical cannabis,” says Fish.
The post Implementing Real Science in Cultivation and Extraction appeared first on Cannabis Industry Journal.
]]>The post QuEChERS 101 appeared first on Cannabis Industry Journal.
]]>
In 2003, a time when only eight states had legalized the use of medical cannabis, a group of four researchers published an article in the Journal of AOAC International that made quite the impact in the residue monitoring industry. Titled Fast and Easy Multiresidue Method Employing Acetonitrile Extraction/Partitioning and “Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction” for the Determination of Pesticide Residues in Produce, Drs. Michael Anastassiades, Steven Lehotay, Darinka Štajnbaher and Frank Schenck demonstrate how hundreds of pesticides could be extracted from a variety of produce samples through the use of two sequential steps: an initial phase partitioning followed by an additional matrix clean up. In the paper’s conclusion, the term QuEChERS was officially coined. In the fourteen years that have followed, this article has been cited over 2800 times. Subsequent research publications have demonstrated its use in matrices beyond food products such as biological fluids, soil and dietary supplements for a plethora of analytes including phthalates, pharmaceutical compounds and most recently cannabis.

The original QuEChERS extraction method utilized a salt blend of 4 g of magnesium sulfate and 1 g of sodium chloride. A starting sample volume of 10 g and 10 mL of acetonitrile (ACN) were combined with the above-mentioned salt blend in a centrifuge tube. The second step, dispersive solid phase extraction (dSPE) cleanup, included 150 mg of magnesium sulfate and 25 mg of primary secondary amine (PSA). Subsequent extraction techniques, now known as AOAC and European QuEChERS, suggested the use of buffered salts in order to protect any base sensitive analytes that may be critical to one’s analysis. Though the pH of the extraction solvent may differ, all three methods agree that ACN should be used as the starting organic phase. ACN is capable of extracting the broadest range of analytes and is compatible with both LC-MS/MS and GC-MS systems. While ethyl acetate has also been suggested as a starting solvent, it is incompatible with LC-MS/MS and extracts a larger amount of undesirable matrix components in the final aliquot.
All laboratories, including cannabis and food safety settings, are constantly looking for ways to decrease their overhead costs, batch out the most samples possible per day, and keep their employees trained and safe. It is not a stretch to say that QuEChERS revolutionized the analytical industry and made the above goals tangible achievements. In the original publication, Anastassiades et al. established that recoveries of over 85% for pesticides residues were possible at a cost as low as $1 per ten grams of sample. Within forty minutes, up to twelve samples were fully extracted and ready to be analyzed by GC-MS, without the purchase of any specialized equipment. Most importantly, no halogenated solvents were necessary, making this an environmentally conscious concept. Due to the nature of the cannabis industry, laboratories in this field are able to decrease overall solvent usage by a greater amount than what was demonstrated in 2003. The recommended starting sample for cannabis laboratories is only one gram of flower, or a tenth of the starting volume that is commonly utilized in the food safety industry. This reduction in sample volume then leads to a reduction in acetonitrile usage and thus QuEChERS is a very green extraction methodology.

As with any analytical method, QuEChERS is not perfect or ideal for every laboratory setting. Challenges remain in the cannabis industry where the polarity of individual pesticides monitored in some states precludes them from being amenable to the QuEChERS approach. For cannabis laboratories looking to improve their pesticide recoveries, decrease their solvent usage and not invest their resources into additional bench top equipment, QuEChERS is an excellent technique to adopt. The commercialization of salt blends specific for cannabis flowers and edibles takes the guesswork out of which products to use. The growth of cannabis technical groups within established analytical organizations has allowed for better communication among scientists when it comes to best practices for this complicated matrix. Overall, it is definitely worth implementing the QuEChERS technique in one’s cannabis laboratory in order to streamline productivity without sacrificing your results.
The post QuEChERS 101 appeared first on Cannabis Industry Journal.
]]>The post Pesticide Analysis in Cannabis and Related Products: Part 3 appeared first on Cannabis Industry Journal.
]]>Despite these challenges, adaptation of methods used by the food safety industry have proved successful for testing pesticides in cannabis. These methods typically rely on mass spectrometric detection paired with sample preparation methods to render the sample clean enough to yield quality data.
Pesticide Analysis Methods: Sample preparation and Analytical Technique Strategy
Generally, methods can be divided into two parts; sample preparation and analytical testing where both are critical to the success of pesticide residue testing and are inextricably linked. Reliance on mass spectrometric techniques like tandem mass spectrometry and high resolution accurate mass (HRAM) mass spectrometry is attributed to the substantial sensitivity and selectivity provided. The sensitivity and selectivity achievable by the detector largely dictates the sample preparation that will be required. The more sensitive and selective the detector, the less rigorous and resource intensive sample preparation can be.
Analytical technique: Gas and Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry
The workhorse approach for pesticide residue analysis involves using gas chromatography and liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) in the ion transition mode. This ion transition mode, often referred to as multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) or selected reaction monitoring (SRM), adds the selectivity and sensitivity needed for trace level analysis. Essentially, a pesticide precursor ion is fragmented into product ions. The detector monitors the signal for a specified product ion known to have originated from the pesticide precursor ion. This allows the signal to be corrected, associated with the analyte and not with other matrix components in the sample. In addition, because only ions meeting the precursor/product ion requirements are passed to the detector with little noise, there is a benefit to the observed signal to noise ratio allowing better sensitivity than in other modes. Even though ion transitions are specific, there is the possibility a matrix interference that also demonstrates that same ion transition could result in a false positive. Multiple ion transitions for each analyte are monitored to determine an ion ratio. The ion ratio should remain consistent for a specific analyte and is used to add confidence to analyte identification.
The best choice for pesticide analysis between gas chromatography (GC) and liquid chromatography (LC) is often questioned. To perform comprehensive pesticide screening similar to the way the food safety market approaches this challenge requires both techniques. It is not uncommon for screening methods to test for several hundred pesticides that vary in physiochemical properties. It may be possible that with a smaller list of analytes, only one technique will be needed but often in order to reach the low limits for pesticide residues both GC and LC are required.

Analytical technique: Sample Preparation
Less extensive sample preparation is possible when combined with sensitive and selective detectors like MS/MS. One popular method is the QuEChERS approach. QuEChERS stands for Quick, Easy, Cheap, Effective, Rugged and Safe. It consists of a solvent extraction/salting out step followed by a cleanup using dispersive solid phase extraction. Originally designed for fruit and vegetable pesticide testing, QuEChERS has been modified and used for many other commodity types including cannabis. Although QuEChERS is a viable method, sometimes more cleanup is needed and this can be done with cartridge solid phase extraction. This cleanup functions differently and is more labor intensive, but results in a cleaner extract. A cleaner extract helps to secure quality data and is sometimes needed for difficult analyses.
The post Pesticide Analysis in Cannabis and Related Products: Part 3 appeared first on Cannabis Industry Journal.
]]>